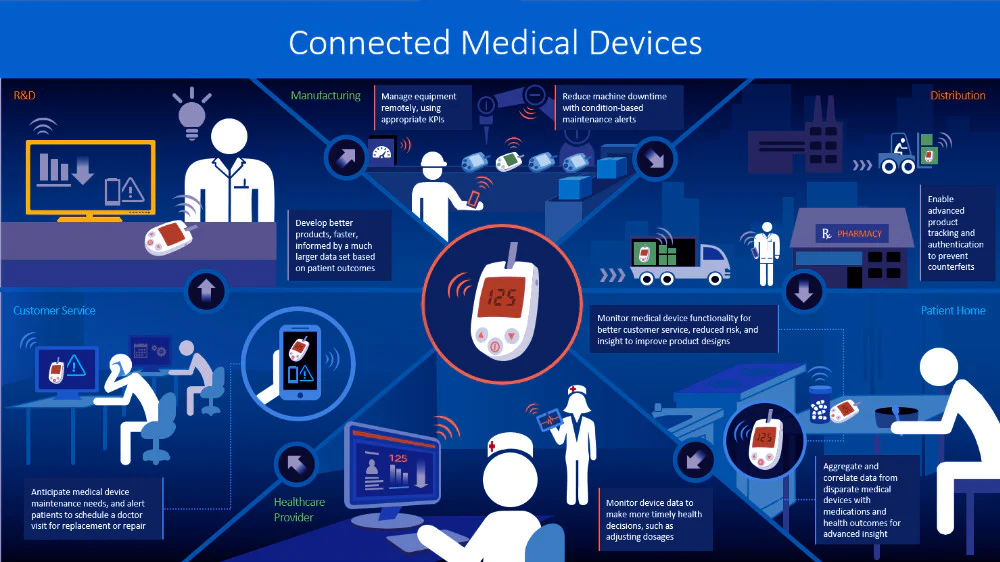
Wearable technology has transitioned from a niche interest to a pivotal force in healthcare, reshaping how we monitor, diagnose, and manage health. As devices become more sophisticated and integrated, their potential to enhance patient care and improve health outcomes grows exponentially. This article explores the transformative impact of wearable technology in healthcare, highlighting its benefits, applications, and future potential.
The Evolution of Wearable Technology
Wearable technology encompasses a wide range of devices that can be worn on the body, including smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical devices. These gadgets collect data on various health metrics, from physical activity and sleep patterns to heart rate and glucose levels. The evolution of these technologies has been driven by advances in sensors, connectivity, and data analytics, enabling more precise and actionable health monitoring.
Enhancing Patient Monitoring and Management
- Chronic Disease Management: Wearable technology is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. For instance, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, helping diabetic patients make informed decisions about their diet and insulin use. Similarly, wearable blood pressure monitors offer constant readings, allowing patients and healthcare providers to track trends and adjust treatments proactively.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: The ability to monitor patients remotely has become increasingly valuable, especially in managing long-term conditions and reducing hospital visits. Wearable devices can transmit data to healthcare providers, facilitating timely interventions and reducing the need for in-person appointments. This not only improves patient convenience but also helps in early detection of potential health issues, leading to better outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- Fitness and Wellness Tracking: For the general population, wearable devices offer insights into physical activity, sleep quality, and overall wellness. Fitness trackers can motivate users to achieve their health goals by providing feedback on exercise routines, step counts, and sleep patterns. This data helps individuals make lifestyle changes that promote long-term health, such as increasing physical activity or improving sleep habits.
Advancing Diagnostic Capabilities
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Wearable technology can play a crucial role in early diagnosis by continuously monitoring vital signs and detecting anomalies. For example, smartwatches equipped with electrocardiogram (ECG) sensors can identify irregular heartbeats that may indicate atrial fibrillation, a condition that could lead to stroke if left untreated. Early detection allows for timely medical intervention, which can significantly improve patient outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Wearable devices contribute to the shift towards personalized medicine by providing detailed insights into an individual’s health status. Data collected from wearables can be used to tailor treatment plans based on specific health patterns and behaviors. This personalization helps optimize therapies, improve adherence, and enhance the effectiveness of medical interventions.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data Privacy and Security: The vast amount of personal health data collected by wearable devices raises concerns about privacy and security. Ensuring that this data is protected against breaches and unauthorized access is crucial. Robust encryption methods, secure data storage, and compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) are essential to maintaining user trust and safeguarding sensitive information.
- Accuracy and Reliability: While wearable technology has advanced significantly, issues related to data accuracy and device reliability persist. Variability in sensor performance and user behavior can impact the quality of data collected. Continuous improvement in sensor technology and calibration methods is necessary to enhance the reliability of wearable devices and their utility in clinical settings.
- Integration with Healthcare Systems: Integrating data from wearable devices into existing healthcare systems and electronic health records (EHRs) remains a challenge. Seamless integration is necessary to ensure that healthcare providers can effectively use wearable data in clinical decision-making. Collaborative efforts between technology developers and healthcare providers are needed to address this integration challenge.
The Future of Wearable Technology in Healthcare
The future of wearable technology in healthcare is promising, with ongoing advancements expected to further enhance its impact. Innovations in sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and data analytics will likely lead to more accurate and insightful health monitoring. Additionally, the increasing adoption of wearables in preventive healthcare and personalized medicine will continue to transform the healthcare landscape.
In conclusion, wearable technology is reshaping healthcare by providing valuable tools for monitoring, diagnosing, and managing health. As the technology continues to evolve, its potential to improve patient outcomes, enhance diagnostics, and promote wellness will only grow. By addressing challenges related to data privacy, accuracy, and integration, wearable technology can realize its full potential in advancing healthcare for all.