The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we interact with technology, offering unprecedented convenience and connectivity. From smart home devices that manage our thermostats and security systems to wearables that monitor our health, IoT technologies are seamlessly integrating into our daily lives. However, this integration brings with it significant privacy concerns that demand careful consideration.
Understanding IoT and Its Privacy Implications
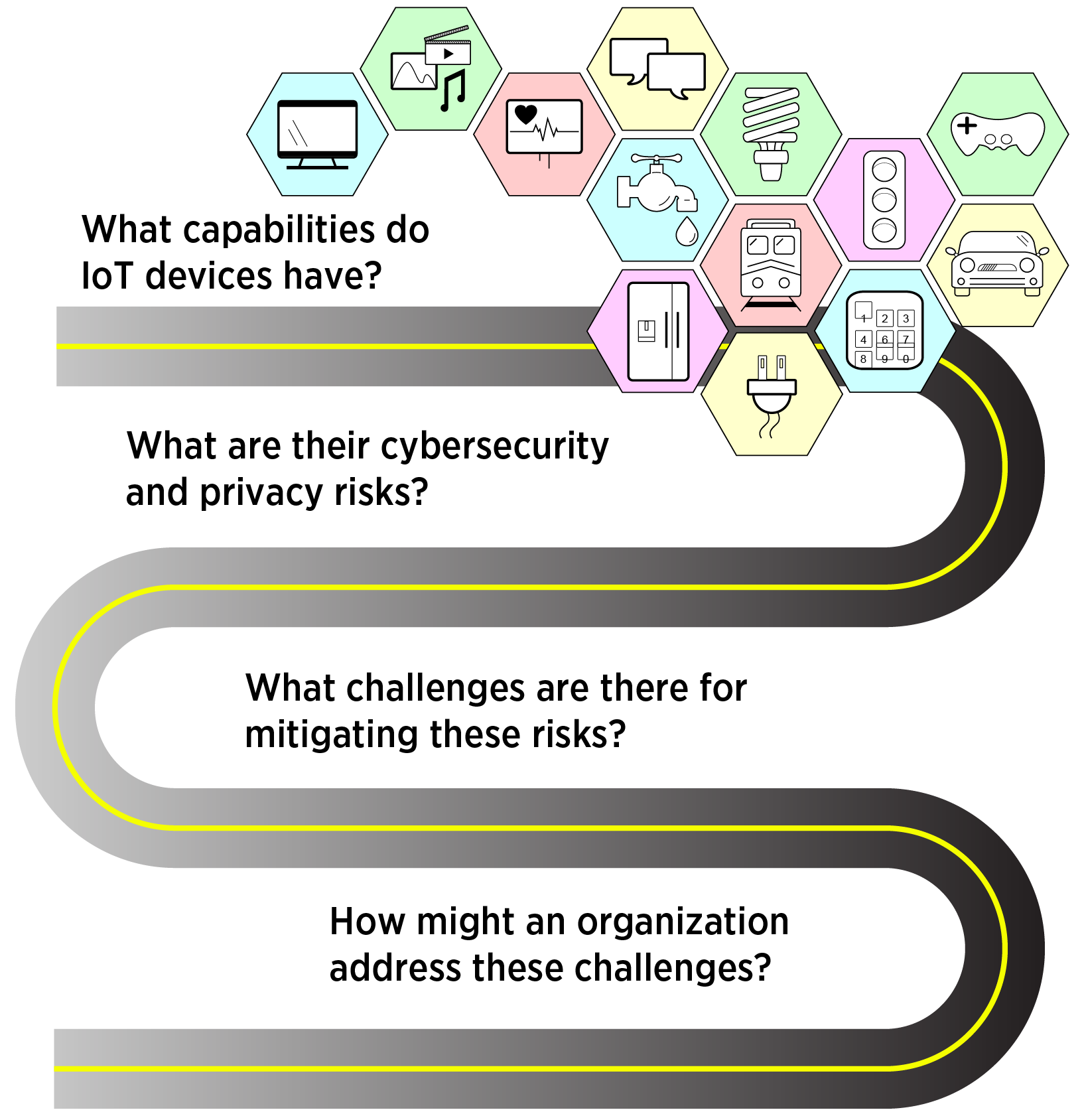
At its core, IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data with each other. These devices collect vast amounts of information, from basic operational data to more sensitive personal details. While this data collection enables enhanced functionality and personalized experiences, it also poses substantial privacy risks.
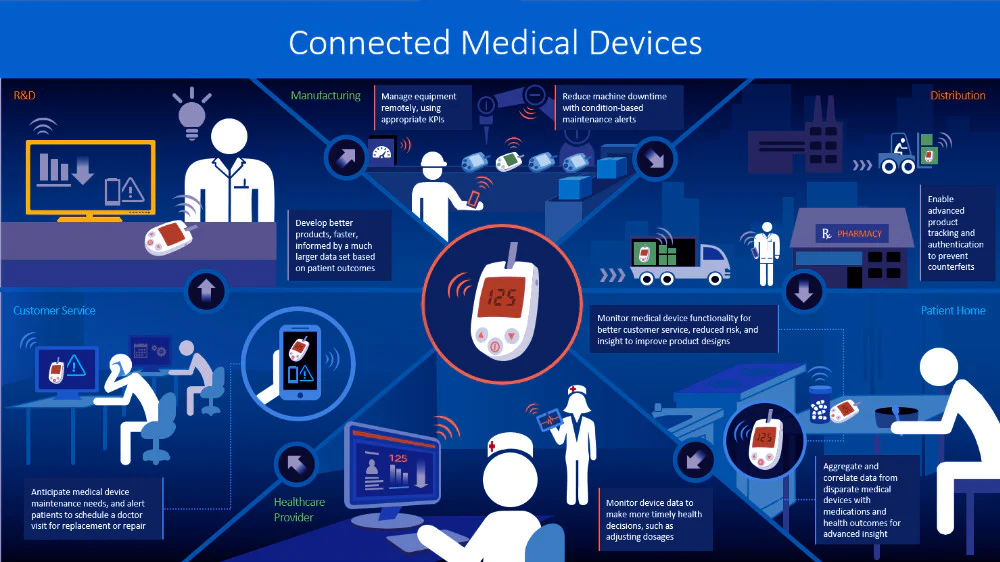
One primary concern is the sheer volume of data being collected. Smart home devices, such as voice assistants and smart cameras, can gather extensive information about daily routines, preferences, and even private conversations. Wearables, like fitness trackers and smartwatches, monitor health metrics and activity levels, creating detailed profiles of users’ physical conditions. This data can be incredibly valuable, but it also presents opportunities for misuse if not properly protected.
Data Security Vulnerabilities
The security of IoT devices is often less robust compared to traditional computing systems. Many IoT devices have limited processing power and storage, making it challenging to implement strong security measures. Additionally, manufacturers sometimes prioritize speed to market over security, leading to vulnerabilities in the devices themselves. This can result in data breaches where sensitive information is accessed or stolen by malicious actors.
Moreover, IoT devices are frequently connected to the internet, creating multiple points of potential entry for cybercriminals. For instance, a vulnerability in a smart thermostat or a security camera could be exploited to gain access to a user’s entire home network. Ensuring the security of these devices requires regular updates and patches, but many consumers may not be aware of or diligent about applying them.
Data Sharing and Third-Party Access
Another privacy issue arises from data sharing practices. Many IoT devices collect data that is then shared with third-party companies, often for purposes like improving service quality or targeted advertising. Users may not be fully aware of how their data is being used or shared, leading to potential breaches of privacy. Privacy policies are often lengthy and complex, and users may not thoroughly read or understand them.
In some cases, the data collected by IoT devices can be sold to data brokers, who aggregate and analyze it for various purposes. This can result in the commodification of personal information, where individuals have little control over how their data is used or who has access to it.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
As IoT technologies continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are struggling to keep pace. Many existing privacy laws do not adequately address the unique challenges posed by IoT devices. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States offer some protections, but they may not fully cover the specificities of IoT data collection and sharing practices.
Ethically, there is a growing need for manufacturers to prioritize privacy by design. This means incorporating robust security measures and transparency into the development process from the outset. Users should also be given clear, accessible options to control their data, including the ability to opt-out of data sharing and delete their information.
Best Practices for Protecting IoT Privacy
To mitigate privacy risks associated with IoT devices, users can adopt several best practices. Firstly, ensuring that devices are updated regularly can help protect against known vulnerabilities. Additionally, configuring device settings to limit data collection and sharing can provide more control over personal information. Users should also be cautious about the permissions they grant to IoT devices and be vigilant about reviewing privacy policies.
In conclusion, while IoT technologies offer incredible benefits, they also bring significant privacy challenges. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, involving both stronger regulatory measures and proactive steps by manufacturers and consumers. By staying informed and vigilant, we can better navigate the complexities of IoT privacy and harness the advantages of connected technology without compromising our personal information.